dask_sparse_mtx¶
Overview¶
This is a simple demo showing how to use dask delayed and dask arrays to multiply sparse matricies loaded in lazily into memory (here, from an sqlite3 database).
Either approach uses dask.delayed to wrap reading tiles of the matrix
into tasks, and then either manually (using
dask_sparse_mtx.dask_delayed_mult()) or using the infrastructure
provided by dask.array (using dask_sparse_mtx.dask_array_mult())
multiplies the two matrices in a tiled manner:
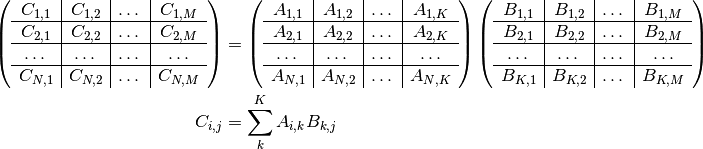
where the multiplication in the second line above is matrix multiplication.
The example can be run as follows (will take a few minutes):
import os
import dask.multiprocessing
import dask_sparse_mtx as dsm
dask.set_options(get=dask.multiprocessing.get)
filename = "test.db"
size = 20000
# create file
dsm.mtxdb_init(filename)
# create matrices and write them; their product
# will be the identity matrix
a = dsm.mtx_permutation(size)
b = dsm.mtx_transpose(a)
dsm.mtxdb_add_matrix_from_dict(filename, 'A', a)
dsm.mtxdb_add_matrix_from_dict(filename, 'B', b)
# smaller tilesize - more parallelism, but more
# overhead from task management
tilesize = 2000
c = dsm.dask_array_mult(filename, 'A', 'B', tilesize)
print c[:10, :10]
if dsm.mtx_is_identity(c):
print "Success!"
os.remove(filename)
And using dask.distributed this computation can be run across several hosts.
Matrix Multiplication¶
Matrix multiplication is performed by either dask_sparse_mtx.dask_delayed_mult()
or dask_sparse_mtx.dask_array_mult():
- Multiply two sparse matrices in the database
using dask.delayed and task parallelism.
Pros: high control over tiles size, distribution Cons: larger memory usage in intermediate steps as
tiles can’t be mutated
-
dask_sparse_mtx.dask_delayed_mult.dask_delayed_mult(dbname, a, b, tilesize)¶ Multiplies two sparse matrices from the matrix db using dask.delayed and task parallelism
TODO: better reduction over intermediate terms
Parameters: - dbname – Filename of the sparse matrix db
- a – Name of matrix A in the db
- b – Name of matrix B in the db
- tilesize – int - size of the (square) tiles read in to do the multiplication
Return type: dictionary of sparse.COO matrix tiles - eg c[(i,j)] is the i, jth tile of product
- Multiply two sparse matrices in the database
by constructing a dask array from the tiles
- Pros: Makes better use of the scheduler, esp for large numbers of tiles
- Don’t have to think about de-tiling final result
Cons: Less control of tiling in intermediate and final stages
-
dask_sparse_mtx.dask_array_mult.dask_array_mult(dbname, a, b, tilesize)¶ Multiplies two sparse matrices from the matrix db using dask.arrays
Parameters: - dbname – Filename of the sparse matrix db
- a – Name of matrix A in the db
- b – Name of matrix B in the db
- tilesize – int - size of the (square) tiles read in to do the multiplication
Return type: sparse.COO - single sparse matrix final result
Sparse Matrix DB¶
These rely on routines for reading/writing the sparse matrices (in COO format) into the sqlite3 db:
- Reads/writes sparse matrices (in COO format) into
- sqlite3 db
-
dask_sparse_mtx.mtxdb.mtxdb_init(filename)¶ Initializes an sqlite3 db for writing sparse matrices.
Parameters: filename – name of sqlite3 db file to create
-
dask_sparse_mtx.mtxdb.mtxdb_add_matrix_from_dict(filename, mtxname, mtxdict)¶ Writes a matrix in COO format to sqlite3 db ‘filename’.
Parameters: - filename – name of sqlite3 db in which to store the matrix
- mtxname – name of matrix (string)
- mtxdict – dict of form (row, col): value containing matrix coordinates and data
-
dask_sparse_mtx.mtxdb.mtxdb_read_chunk(filename, mtxname, rows=None, cols=None)¶ - Reads a whole or partial matrix from a sqlite3 db into
- a mod:sparse COO matrix
Parameters: - filename – name of sqlite3 db from which to read the matrix
- mtxname – name of matrix (string)
- rows – optional tuple containing the slice of rows to read in, eg rows=(100,200) will read in rows 100..199. If None, will read all rows
- cols – as with rows, but for columns
Return type: mod:sparse COO matrix
-
dask_sparse_mtx.mtxdb.mtxdb_matrix_shape(filename, mtxname)¶ Returns the shape of a sparse matrix in the db.
Parameters: - filename – name of the sqlite3 db in which the matrix is stored
- mtname – name of the matrix(string)
Return type: (rowmin, rowmax, colmin, colmax): min/max of rows and columns
Sparse Matrix Helper Methods¶
And finally there are helper routines for creating simple permutation matricies useful for tests:
- Routines for simple COO matrices expressed as dicts
- {(row, col): value } for test problems
-
dask_sparse_mtx.mtx.mtx_permutation(size)¶ Returns a matrix in COO format as a dictionary describing a permutation matrix.
Parameters: size – size of (necessarily square) permutation matrix Return type: dictionary of (row, col): val matrix entries
-
dask_sparse_mtx.mtx.mtx_transpose(dictmtx)¶ Returns transposes of a matrix in COO format (expressed as a dict).
Parameters: dictmtx – dictionary containing COO matrix Return type: dictionary of (row, col): val matrix entries
-
dask_sparse_mtx.mtx.mtx_is_identity(mtx)¶ Returns True if matrix (dict or sparse.COO) is the identity matrix False otherwise
Parameters: mtx – sparse.COO or dict matrix Return type: Bool: True if identity